Optimizing the Use of Biodosimetry Tools in a Mass Casualty Incident When Surge with High Throughput is Necessary
 |
Time for Sample Preparation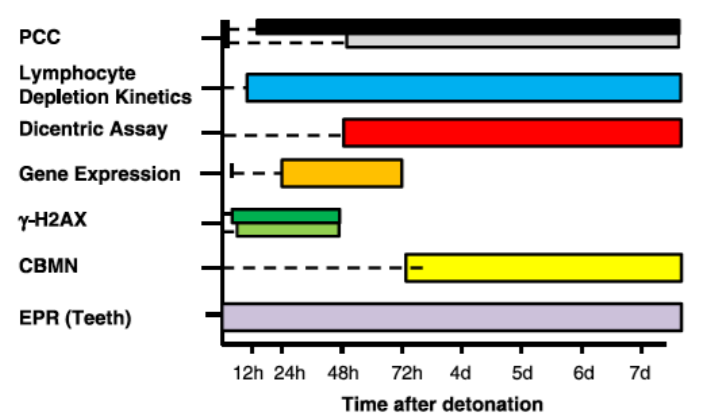 ---- Time for sample preparation and analysis "Time-phased comparison of currently available dosimetry methods out to one week after detonation. Dotted lines represent time needed for sample preparation to occur before any results become available." PCC: Premature Chromosome Condensation CBMN: Cytokinesis Block Micronucleus EPR: Electron Paramagnetic Resonance "Note:
Source: Sullivan JM et al., Assessment of Biodosimetry Methods for a Mass Casualty Radiological Incident: Medical Response and Management Considerations. Health Phys. 2013;105(6):540-554, See Figure 2. [PubMed Citation] Dose Range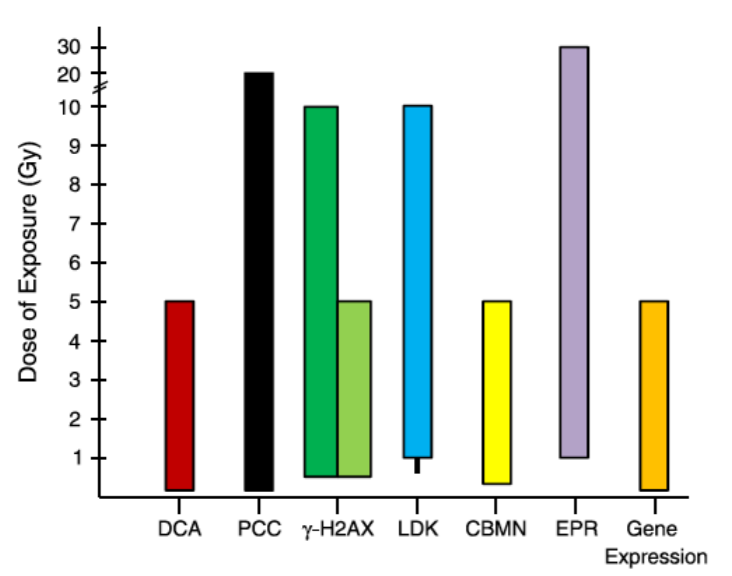 Dose range in which the indicated assays are able to estimate absorbed radiation dose. DCA: Dicentric Chromosome Assay PCC: Premature Chromosome Condensation LDK: Lymphocyte Depletion Kinetics CBMN: Cytokinesis Block Micronucleus EPR: Electron Paramagnetic Resonance
Source: Sullivan JM et al., Assessment of Biodosimetry Methods for a Mass Casualty Radiological Incident: Medical Response and Management Considerations. Health Phys. 2013;105(6):540-554, See Figure 1. [PubMed Citation] Multiple Parameters
Source: Sullivan JM et al., Assessment of Biodosimetry Methods for a Mass Casualty Radiological Incident: Medical Response and Management Considerations. Health Phys. 2013;105(6):540-554, See Table 1. [PubMed Citation] |

