Ionization - Animations

 |
When it penetrates tissue, radiation alters the cells. Effects, known as early effects, appear when too many cells have been destroyed. Other, late effects may occur if certain altered cells proliferate uncontrollably and lead to cancer. 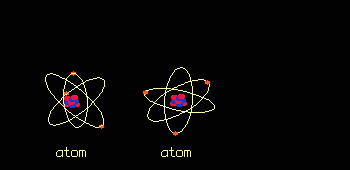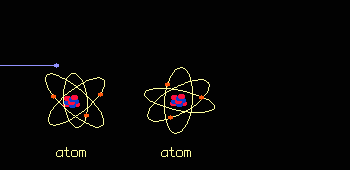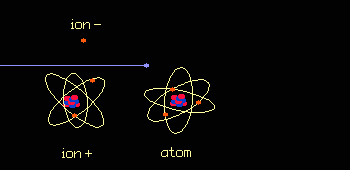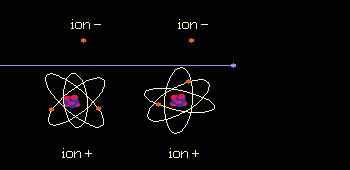 Radiation is Ionizing: it strips atoms of electrons. Each collision produces two ions: a free electron which is negatively charged and an atom which has lost an electron and is positively charged. 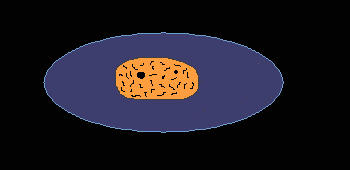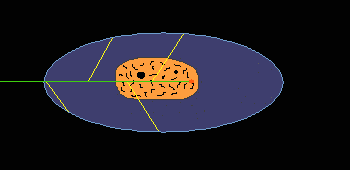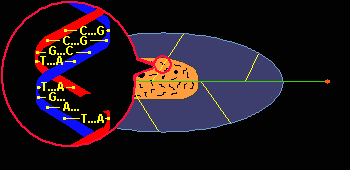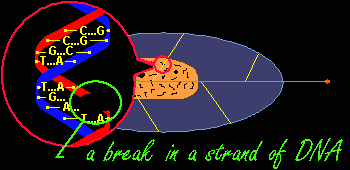 Ionizing an atom inside a molecule damages the molecule. The cell reproduction process is affected most when large molecules such as DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) are damaged. 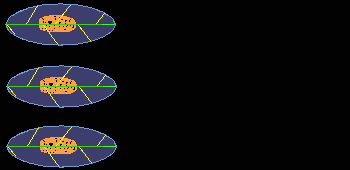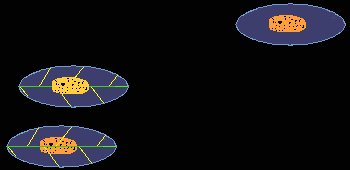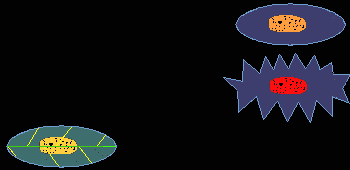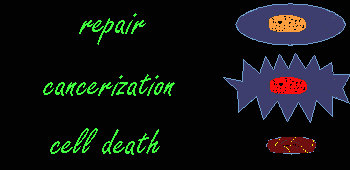
Adapted from Biological effects (Radior, IAEA, European Commission, CEPN) |

